Input cell
One Ring to rule them all...
An input cell is a multi-tool. By default, it assumes Wolfram Language as input; however, this can be changed using a directive in the first line. See Markdown, JavaScript, WLX, HTML, Slides, and others.
For example:
Think of it like an anonymous file.
After typing, press Shift-Enter to make the magic happen.
When you start typing, the following occurs:
- Each character is sent to a server and the cell is updated (autosaving every 300 ms).
- The editor attempts to detect the language or cell type.
- Based on (2), it applies syntax highlighting, autocompletion, and other plugins.

Cell Properties
Click on the ... (more icon) on the right side of a cell group to access input cell properties.
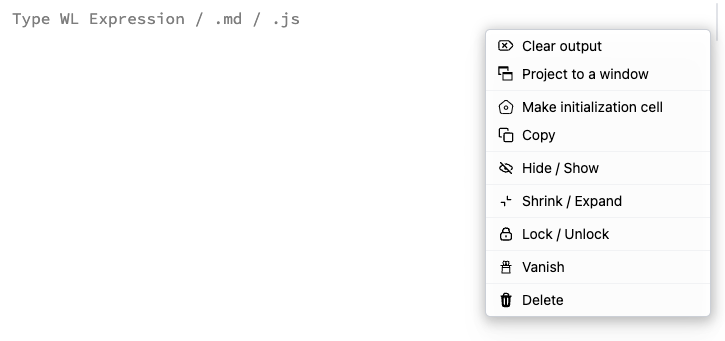
This affects the entire cell group (input + output cells). The following transformations are available:
- Project to a window – evaluates the cell and displays the first output in a separate window.
- Make initialization cell – marks an input cell to evaluate automatically when the notebook opens (shown with a green dot in the top-right corner).
- Copy – compresses the cell group into a gzip-compressed string expression. Paste it into a new input cell.
- Hide / Show – hides the input cell while keeping the output visible. Shortcut:
Cmd+2 / Alt+2, or use the arrow icon on the left. - Shrink / Expand – fades large text to show only a preview. The cursor can still enter the area.
- Lock / Unlock – makes the input read-only and limits editing options.
- Vanish – makes the entire cell group invisible and uneditable. Output code (JS/HTML) still runs but is hidden. Only visible in
Expert Mode(found in Settings). Useful for templates.
Wolfram Language
Syntax Highlighting & Symbol Tracking
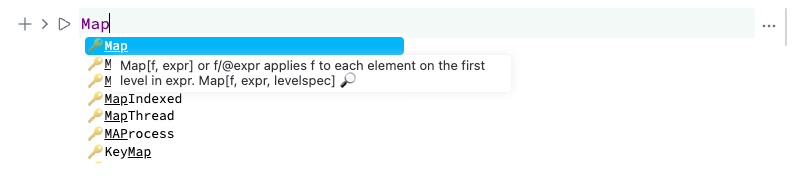
Wolfram Language autocomplete and highlighting can be extended using external packages.
Once a symbol is defined in the `Global`` context of a Wolfram Kernel session, it appears in the autocomplete window and is shared across open notebooks.
At startup, the Wolfram Kernel loads all imported packages, reads ::usage directives for defined symbols, and periodically refreshes this info upon Get or Needs commands.
Syntax Sugar
All equations typed in the editor are compatible with WL kernels, including wolframscript. Syntax sugar is localized within comments.
For example:
becomes:
(*SqB[*)Sqrt[2\[Pi]](*]SqB*)
This ensures compatibility outside the WLJS ecosystem.
You don't need a mouse to construct or edit complex equations.
Unlike Wolfram Mathematica, our StandardForm output is always compatible with InputForm.
Common equation editing shortcuts:
Ctrl-2– square rootCtrl-/– fractionCtrl--– subscriptCtrl-6– superscriptESC + ..– Greek letters (pick from autocomplete)Ctrl-=- Semantic interpretation
Editor shortcuts:
Alt+/,Cmd+/– comment line- Hold
Alt– multiple carets Cmd/Ctrl+F– search current cell
Cursor navigation:
ArrowLeft/ArrowRight– character movementCtrl-ArrowLeft/Ctrl-ArrowRight– word movementCmd-ArrowLeft/Cmd-ArrowRight– start/end of lineArrowUp/ArrowDown– move linesCmd-ArrowUp/Cmd-ArrowDown– start/end of documentCtrl-ArrowUp/Ctrl-ArrowDown– page up/downHome/End– line boundariesCtrl-Home/Ctrl-End– document boundariesEnter– new line with indentCtrl-a/Cmd-a– select allBackspace/Delete– delete charactersCtrl-Backspace/Ctrl-Delete– delete wordsCmd-Backspace/Cmd-Delete– delete to line start/end
Advanced movements:
Alt-ArrowLeft/Alt-ArrowRight– move by syntax elementAlt-ArrowUp/Alt-ArrowDown– move linesShift-Alt-ArrowUp/Down– copy linesEscape– simplify selectionAlt-l– select lineCtrl-i– select parent syntaxCtrl-[/Ctrl-]– indent less/moreCtrl-Alt-\\– indent selectionShift-Ctrl-k– delete lineShift-Ctrl-\\– go to matching bracketShift-Alt-a– toggle block comment
EMACS-style bindings (macOS):
Ctrl-b– move leftCtrl-f– move rightCtrl-p– move upCtrl-n– move downCtrl-a– start of lineCtrl-e– end of lineCtrl-d– delete forwardCtrl-h– delete backwardCtrl-k– delete to line endCtrl-Alt-h– delete word backwardCtrl-o– split lineCtrl-t– transpose charactersCtrl-v– page down
For integrals, derivatives, and series, use the Command Palette to insert special characters.
Features like DateObject, Graphics, and many other familiar Mathematica features are supported. See Symbolic Programming for details.
If an output is too large, it may be truncated or converted into a temporary symbol to reduce editor load.
Custom symbol representations (like in Mathematica) are possible via MakeBoxes. See:
Access to Documentation
Click the 🔎 icon in the autocomplete window to open the documentation for a symbol in a new tab.
Morph Output Cell into Input
If you modify a Wolfram Language output cell, it will automatically be converted into a new input cell.
Auto-upload Files
Drag and drop files into the editor or paste media from the clipboard. You can always access clipboard contents using ReadClipboard.
Other Languages
Most other languages supported as input also provide:
- File auto-upload or clipboard media import
- Autocomplete
- Syntax highlighting and code parsing (beyond tokenizing)