Timeline
AF provides a GUI element for timing and adjusting the events on the timeline filling some gaps between programmatic approach for animations and visual like in a typical video editor:
You are still working with AsyncFunction functions. Timeline is an external addition to that.
Quick start
Let's create a timeline:
Needs["AnimationFramework`"->"af`"];
t = af`TimelinedAnimation[animationFunction];
t
Use Projector on the timeline input cell to work with in in a separate window
There are some key aspects of working with a timeline:
- The duration of your playback is defined by the total time needed for executing your animationFunction (which has to be Asynchronous Function)
TimelinedAnimationhasHoldFirstattribute and PLAY button releases it and evaluates animation function symbol provided. I.e. when you update the definition ofanimationFunction, you do not need to reevaluateTimelinedAnimation- Seeking the position on the timeline is done via artificially speeding up time of the scene, since animation function may have internal states.
- Use PauseAsync with
sceneargument provided, otherwise the animation will be un-synced with the timeline.
Now define a basic animation sequence for now without a direct connection with a timeline:
animationFunction = AsyncFunction[scene, Module[{d},
d = af`AddTo[scene, {
Opacity[#o],
Translate[
Rotate[
Rectangle[{-0.5,-0.1}, {0.5,0.1}]
, #r]
, #c]
}, {
"o" -> 0.,
"r" -> 0.,
"c" -> {0,0}
}];
af`Animate[scene, d, {"o" -> 1.0,"r" -> 3.14}, "Ease", 1.0] // Await;
PauseAsync[scene, 0.4] // Await;
af`Animate[scene, d, {"c"->{0.5,0.5}}, "Ease", 1.0] // Await;
af`Animate[scene, d, {"c"->{-0.5,0.5}, "r"->4.2}, "Ease", 1.0] // Await;
af`Animate[scene, d, {"c"->{0.5,-0.5}}, "Ease", 1.0] // Await;
af`Animate[scene, d, {"c"->{0.,0.}, "o"->0., "r"->0}, "Ease", 1.0] // Await;
af`Remove[d];
]];
Now hit PLAY button:

When focused on the timeline:
Spacebar- play/pause
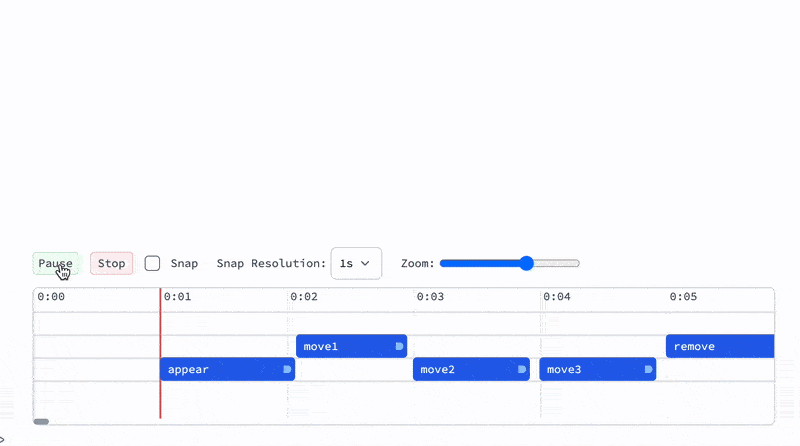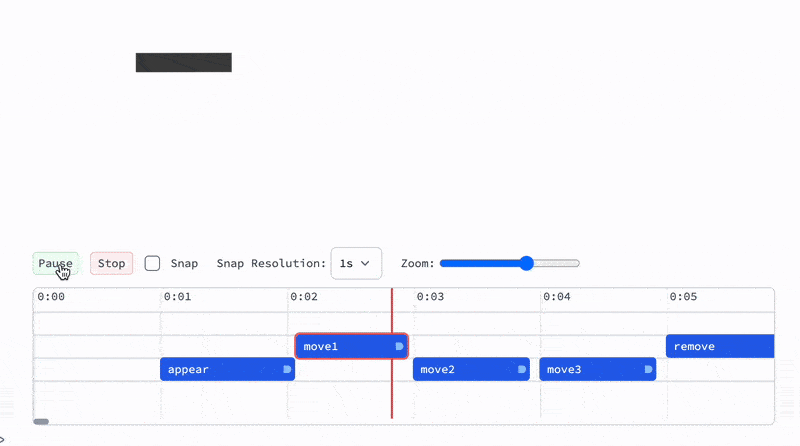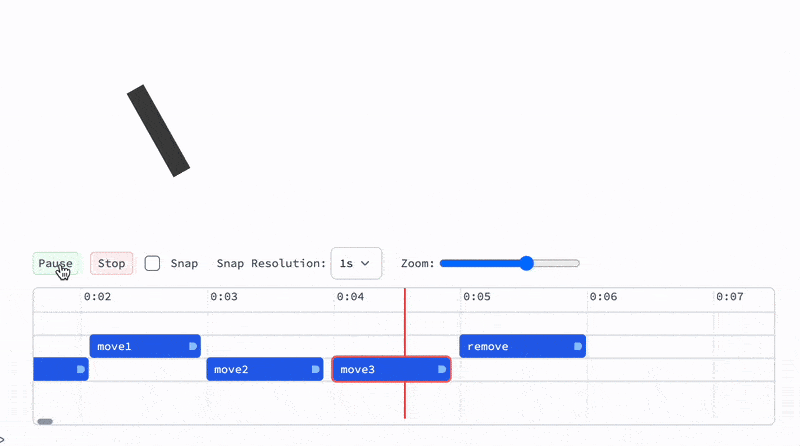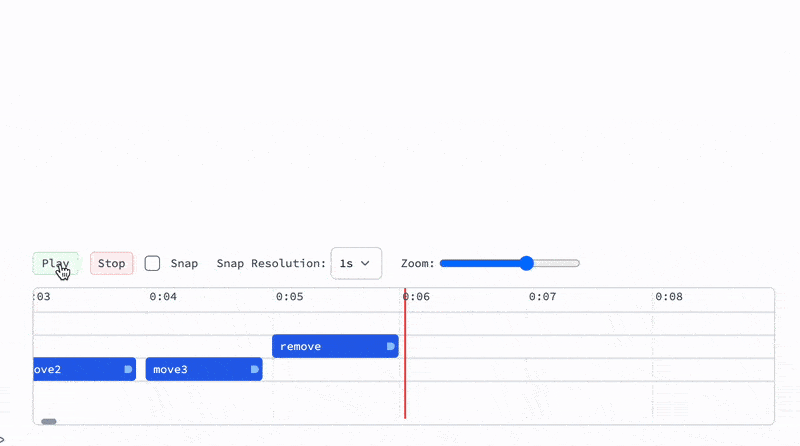
Time markers
To place a time marker - double click:

- All marker must have a unique label
- Double click on a marker to remove it
- Each marker has a duration, you can change it by dragging a gizmo on the right
- Timeline rows have no effect and exists only for the user convenience in placing overlapping markers
A user can can reference the markers from Scene object in two possible ways in the animation function:
- As a pause
wait for the marker
af`Marker[scene, "M1"] // Await;
wait for the end of the marker
af`Marker[scene, "M1", "End"] // Await;
- As a quantity
af`Marker[scene, "M1", "Duration"]
This will return a number in seconds.
Example
Let us transform our previous animation to use marker events
animationFunction = AsyncFunction[scene, Module[{d, u},
d = af`AddTo[scene, {
Opacity[#o],
Translate[
Rotate[
Rectangle[{-0.5,-0.1}, {0.5,0.1}]
, #r]
, #c]
}, {
"o" -> 0.,
"r" -> 0.,
"c" -> {0,0}
}];
af`Marker[scene, "appear"] // Await;
af`Animate[scene, d, {"o" -> 1.0,"r" -> 3.14}, "Ease", af`Marker[scene, "appear", "Duration"]] // Await;
af`Marker[scene, "move1"] // Await;
af`Animate[scene, d, {"c"->{0.5,0.5}}, "Ease", af`Marker[scene, "move1", "Duration"]] // Await;
af`Marker[scene, "move2"] // Await;
af`Animate[scene, d, {"c"->{-0.5,0.5}, "r"->4.2}, "Ease", af`Marker[scene, "move2", "Duration"]] // Await;
af`Marker[scene, "move3"] // Await;
af`Animate[scene, d, {"c"->{0.5,-0.5}}, "Ease", af`Marker[scene, "move3", "Duration"]] // Await;
af`Marker[scene, "remove"]//Await;
af`Animate[scene, d, {"c"->{0.,0.}, "o"->0., "r"->0}, "Ease", af`Marker[scene, "remove", "Duration"]] // Await;
af`Remove[d];
]];
And then place those markers on the timeline:
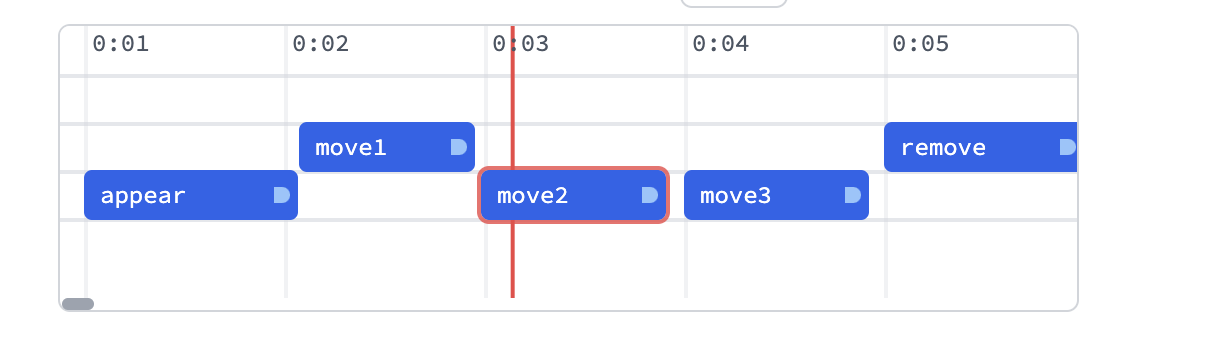
Here is serialized version of all markers from the screenshot above:
<|"move1"-><|"uid"->"move1","time"->2.0757575757575757`,"duration"->0.8787878787878788`,"track"->48|>,"appear"-><|"uid"->"appear","time"->1,"duration"->1.07`,"track"->72|>,"move2"-><|"uid"->"move2","time"->2.9846153846153847`,"duration"->0.9242424242424242`,"track"->72|>,"move3"-><|"uid"->"move3","time"->4,"duration"->0.9242424242424242`,"track"->72|>,"remove"-><|"uid"->"remove","time"->5,"duration"->1,"track"->48|>|>
See how to restore / store markers position in the section Export markers.
Now if you hit a playback button it will play the animation according to your time markers:
Export markers
Access the object t created by TimelinedAnimation animation expression
t["TimeMarkers"]
Restore markers
To import time markers to a new scene or TimelinedAnimation provide "TimeMarkers" options. For example:
import to the scene
s = af`Scene["TimeMarkers" -> ...];
import to the scene in TimelinedAnimation
t = af`TimelinedAnimation[
animationFunction, "TimeMarkers" -> ...
];
import to recorder object
r = af`RecordAnimation[
animationFunction, ImageSize->Large, FrameRate->120,
"TimeMarkers" -> ...
];
Recording
- Export your existing markers following Export markers
- Following the guide Recording provide an options to
RecordAnimationexpression (see Import markers) with exported timeline markers
Voice-over
You can record voice-overs directly to the timeline:
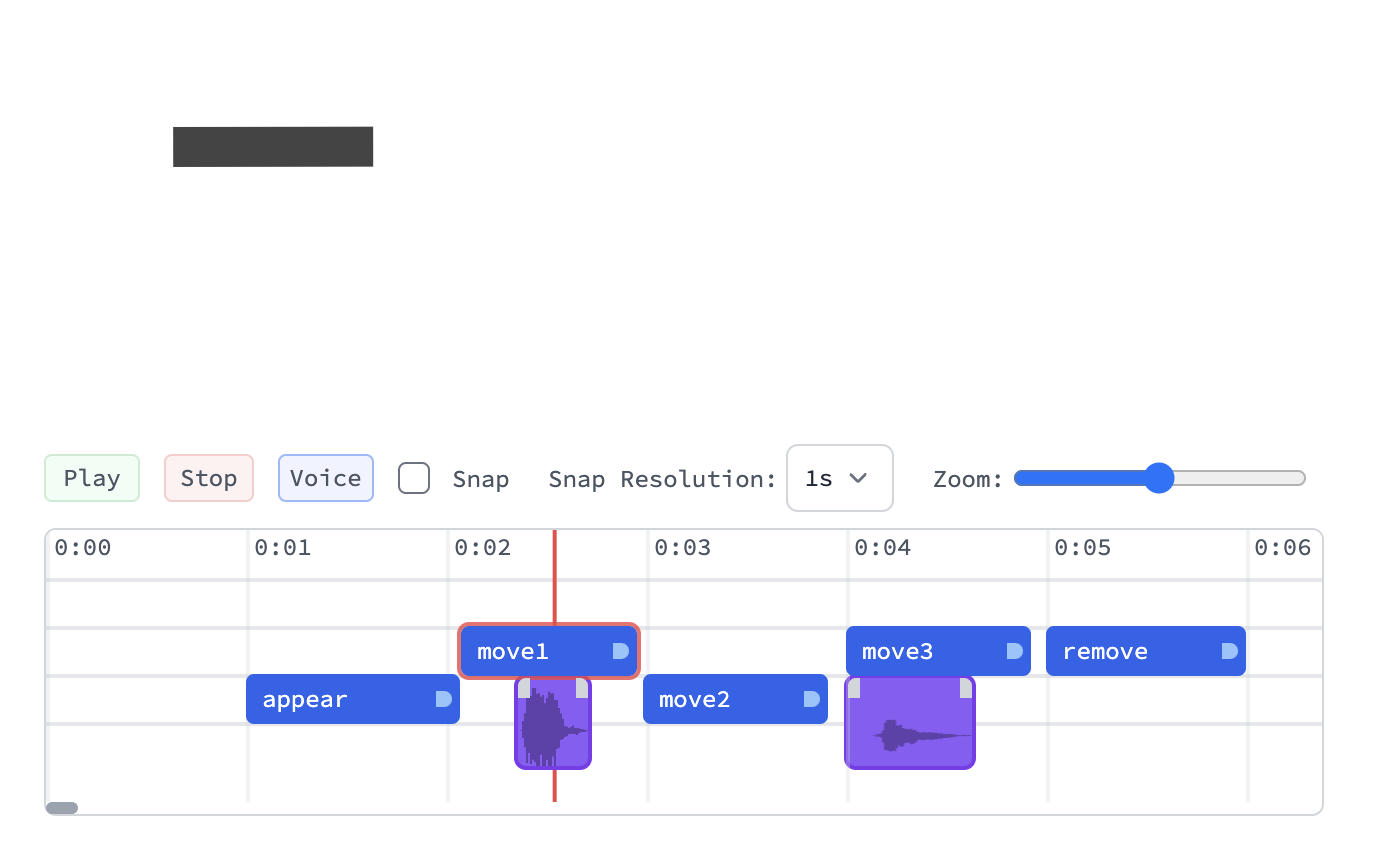
In general it does not matter on which track you place it. Voice clips do not interferer with regular time markers and has to be exported / imported separately.
This functionality serves a purpose of roughly aligning the timing of your animation with your audio narratives, which can be later polished in a professional video editing software.
Recording
Find a place on a timeline and hit Voice button to start recording. Press stop to stop it.
Exporting
To export you can simply read a property of a timeline object:
clips = t["AudioClips"]
Then you can merge it into a single audio file for later production:
af`AudioFromClips[clips]
This will contain an Audio object, which can be exported to be used in other video-editing programs.
Restoring
To restore clips for a new session or a timeline object - provide clips as an options to the constructor:
t = af`TimelinedAnimation[
animationFunction, "TimeMarkers" -> ...,
"AudioClips" -> clips
];